Defining, Measuring, and Improving Employee Performance
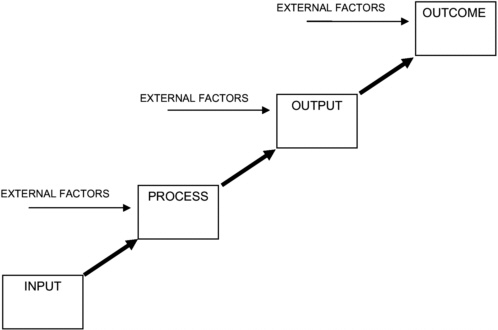
Performance measures can be categorized into three basic groups: input/process measures, output measures, and outcome measures.
Input/Process Measures
Inputs are the budgetary resources, human capital,
materials, and services, and facilities and
equipment associated with a goal or objective.
Process measures are the functions and activities
undertaken that are geared toward accomplishing
an objective.
Examples of input measures:
Resource Requirements: These measures track the re sources required to accomplishthe security program mission:
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) employees, contract support, and training; FSL determination and risk assessments;
Countermeasure installation, maintenance, testing, evaluation and replacement; and Overall Security Program Management (salaries, IT cost, administrative cost).
Output Measures
Outputs are the products and services produced
by the organization and generally can be observed and measured. Efficiency is a measure of the relationship between an organization’s inputs/processes and its outputs.
The following are examples of output measures
-
Security assessments completed versus planned -A core component of a physical security program is the scheduling of initial and recurring risk assessments.
-
Countermeasures deployed: This measure reflects how well the deployment of countermeasures is managed throughout the procurement, installation, and acceptance cycle.
-
This measure focuses on accomplishing an established
schedule for testing countermeasures to determine how well they are working.
-
Incident Response Time:
This measure is suitable for a number of security related requirements.
Security Activity Metric
This metric measures items such as:
Visitors
Alarm responses
Door openings
Material bearer passes
Security incidents
Officer Performance Metric Panel
This metric measures several aspects of a contract security organizations performance. This metric includes items such as:
Employee turnover
Employee involved safety incidents
Safety and security incidents on the client property
Response time
Safety assists such as employee escorts, charging dead batteries, etc.
Number of training conducted for officers on site
Post audits
Security-Safety Metric
The security-safety metric was intended to detect events that affected the overall safety at a facility. These events included:
Water leaks
Reckless activity
On-site drug use
Workplace injuries resulting from slips, trips, and falls.
Security Incident Metrics
This metric is fairly straight forward. It counts and analyzes the number and type of security incidents at a facility.
Loss Reduction/Security Cost Metric
This particular metric primarily focuses on shrinkage and the effect that security has on these losses. This metric can be directly linked to the cost savings for the customer. It specifically measures:
Stock discrepancy
The cost of security as a percentage of sales